|
Dew Math for .NET
|
|
Dew Math for .NET
|
Single-rate finite, linear convolution of two sequences.
Calculate the single-rate finite, linear convolution of two sequences. The results are stored in the calling vector. The argument names X and H ar chosen to suggest FIR filtering. The result of the convolution is defined as follows:
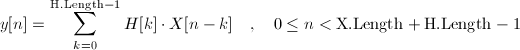
This finite-length convolution is related to infinite-length by:
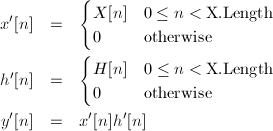
In the above equations, x'[n] and h'[n] are the zero-padded (infinite-length) versions of x[n] and h[n]; y'[n] is the infinite-length output version of y[n]. Then y'[n] is zero everywhere except over:
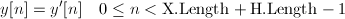
The optional Buffer parameter can be specified to prevent repeated allocation and freeing of memory by the function when both X and H are not complex. If the Buffer parameter is left to be nil, the function will allocate and free required memory internally. If the parameter is not null, the object will be sized and can be reused on consecutive calls without triggering memory reallocation.
Avoding memory reallocations is crucial for multithreaded algorithms.
|
Copyright (c) 1999-2024 by Dew Research. All rights reserved.
|
|
What do you think about this topic? Send feedback!
|